A cheque is an unconditional order addressed to a banker, signed by the person who has deposited money with a banker, requesting him to pay on demand a certain sum of money only to the order of the certain person or to the bearer of the instrument.
Also See: Jaiib Study Material PDF Notes Papers Mock Tests Videos
📚 JAIIB Study Resources 📚
👉 Check Here
👉 Check Here
👉 Check Here
👉 Get Tests Here
👉 Check Here
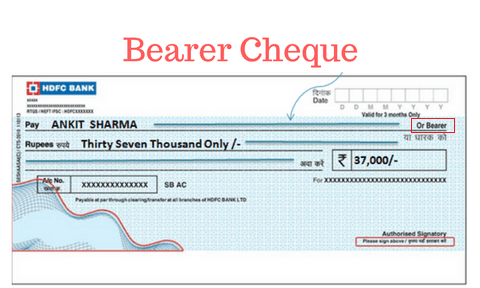
Bearer Cheque
A cheque that is payable to a person whosoever bears is called a bearer cheque.
- The cheque sometimes can be made payable to “Cash” or bearer or made payable to a specific name, for example, “bujji Sekhar or Bearer”.
- This cheque is payable by the drawee bank over the counter to the Bearer or presenter of the cheque.
- A Bearer cheque can be negotiated or passed to another person by mere delivery. In other words, the holder (or the Transferer), when giving it to another person need not endorse the cheque.
- No identification is needed when a bearer cheque is presented for encashment. However, in normal banking practice, where the amount of the cheque is substantial, the identity of the encasher is insisted on.
- A bearer cheque can be collected by the bank for credit to anyone’s account
- In banking practice, the need for the encasher’s signature on the back of the cheque is merely to evidence that the encasher has received the money from the bank.
CHECK IT OUT: JAIIB MAY 2023 ONLINE CRASH COURSE





I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is attractive, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an impatience over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike.
I prepared the topic Cheques and its types in Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881 from your study material. Explained very well. Thanks.
Get prepare the topic cheques and its types with your study material. I also read some articles on that which could help me so much. The link of that article is here https://learningsessions.in/cheques-and-its-types-in-negotiable-instrument-act-1881/